
- #Microsoft azure storage explorer powershell for free#
- #Microsoft azure storage explorer powershell how to#
- #Microsoft azure storage explorer powershell code#
- #Microsoft azure storage explorer powershell windows#
#Microsoft azure storage explorer powershell for free#
Related: Your Options for Getting Microsoft Azure for Free Building an Azure Environmentīefore using blob storage to store your files, you’ll first need to import PowerShell Core modules, connect with your Azure Subscription, and build an Azure environment.ġ. Azure Subscription – There are multiple ways to use specific Azure Resources for little to no cost.AzCopy Executable downloaded and accessible.Az PowerShell Module installed into your PowerShell 7 environment.If you’d like to follow along, be sure you have the following installed and available. This tutorial will be a hands-on demonstration. Hosting a Web Page on Public Internet from Blob Storage.
#Microsoft azure storage explorer powershell windows#
If you open windows explorer or powershell again, the deleted folders appear again, they are like cockroaches. The additional trick on this solution is that you need to immediately restart the machine. Using RegEdit, open the following registry key and delete the folders for each mapping: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MountPoints2 You need to remove the mappings directly in the registry. Strange because it describes a completely different reason for the error, but the solution works. I end up finding the solution in a strange documentation from Microsoft.
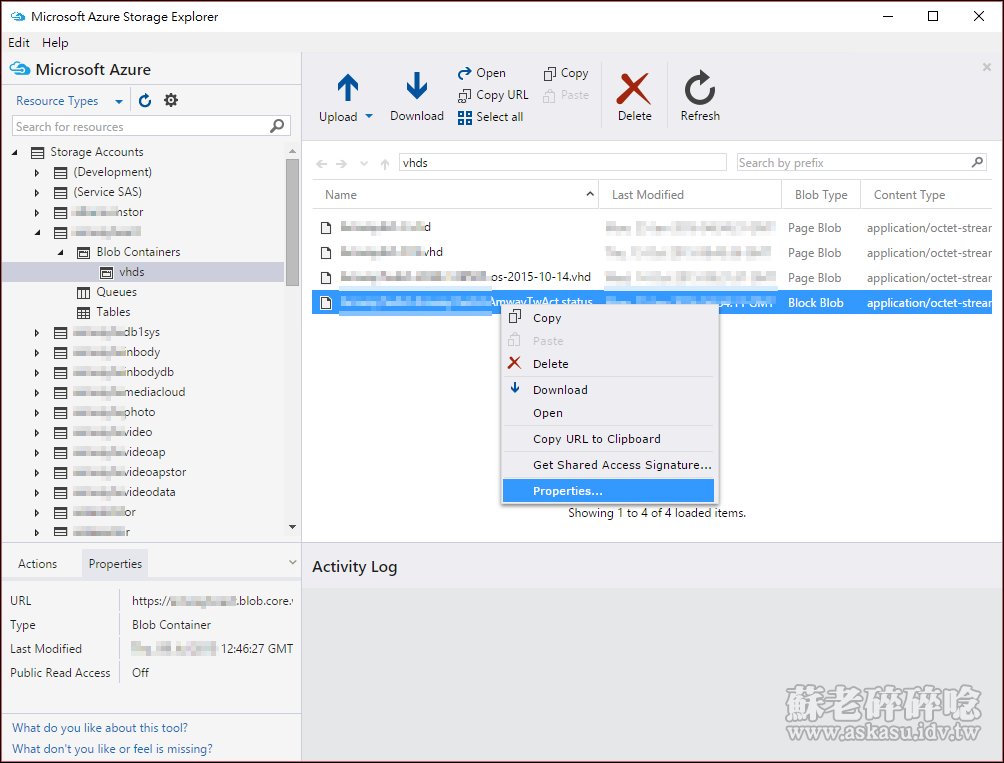
#Microsoft azure storage explorer powershell how to#
I found almost no information about how to fix this, so here it is. What gave me the idea to write this article was exactly the fact I faced a huge error when handling the mappings in a wrong way. One example is that if you execute the script with powershell running as administrator, you will not see it in a regular windows explorer window. The mapping is created for the user who executes the script and only for this user. It’s specially important to remember you can’t delete or disconnect the mapping using traditional OS tools, you need to use Remove-PSDrive cmdlet in Powershell It’s not for everyone You can discover more about Powershell drives on this link These mappings are called Powershell drives. You can’t managed it using the regular tools for a network mapping.
#Microsoft azure storage explorer powershell code#
This mapping created through the PowerShell code is not your regular network mapping. Let’s analyse this and discover how to avoid some mistakes. There are some interesting internal tricks related to the file share mapping. We need to provision an Azure AD Directory Services to use Azure authentication with SMB.ĭrive letter: You can choose the drive letter which will be used for the mapping on your machine. However, Azure AD doesn’t work with SMB out-of-the-box. Azure Authentication is way better option than the storage key. Once we choose these options, the script is changed to use our choices.Īuthentication: We can choose if we will use Azure AD authentication or the storage account key. There are two configuration options we can choose. We will immediately have a new network mapping pointing to our file share on Azure. We can open PowerShell ISE, copy/paste the script from the portal to ISE and execute. Azure itself will provide us with a script to create the mapping on Windows, Linux or Mac.įor windows, it’s a powershell script. On the file share menu, we can select the option Connect. This quota has only two possible files: 5tb or 100tb.Ĭreate the mapping is very easy. The storage account also has a quota for all the file shares.

Using the file share menu you can click the option Edit Quota to change this limit. The default quota is 6GB, which is quite small. File Share QuotaĮach file share has a quota. If you do it wrong, it can cause a lot of trouble. There are some tricks when mapping an azure file share to the local machine. Of course, this is an oversimplification. This means when we use file shares we can map them directly to our file system and work with them using Windows Explorer, as any other network share. While blob containers use REST, file shares can use REST and SMB. The main difference between these services is the protocol used to access them. These are two different services provided by them, but you probably already know that. Storage Accounts allow you to create blob containers or file shares. Azure Storage: Mapping File Shares and Powershell drives - Simple Talk Skip to content


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
